ROME
1,100 BC – 476 BC
According to ancient Roman tradition it was in 753 BC when Romulus and Remus founded the city of Rome. The Romans spread throughout the Mediterranean basin and much of Europe. And through the years, during the imperial period, Roman control extended to unthinkable limits.
Roman architecture was universal even thought they did not follow constructive ideals but, otherwise, stability, functionality and magnificence were key words that defined its architecture. The most singular technical advance was the coverage of large public spaces with arches, vaults or domes, and their huge discovery was concrete.
About their architecture, we can divide it in 4 blocks: religious buildings, civil works, public buidings and private buildings.
RELIGIOUS BUIDINGS
- TEMPLE
When it came to building, the Romans are related to the naturalism, vitality and energy of the Etruscans.
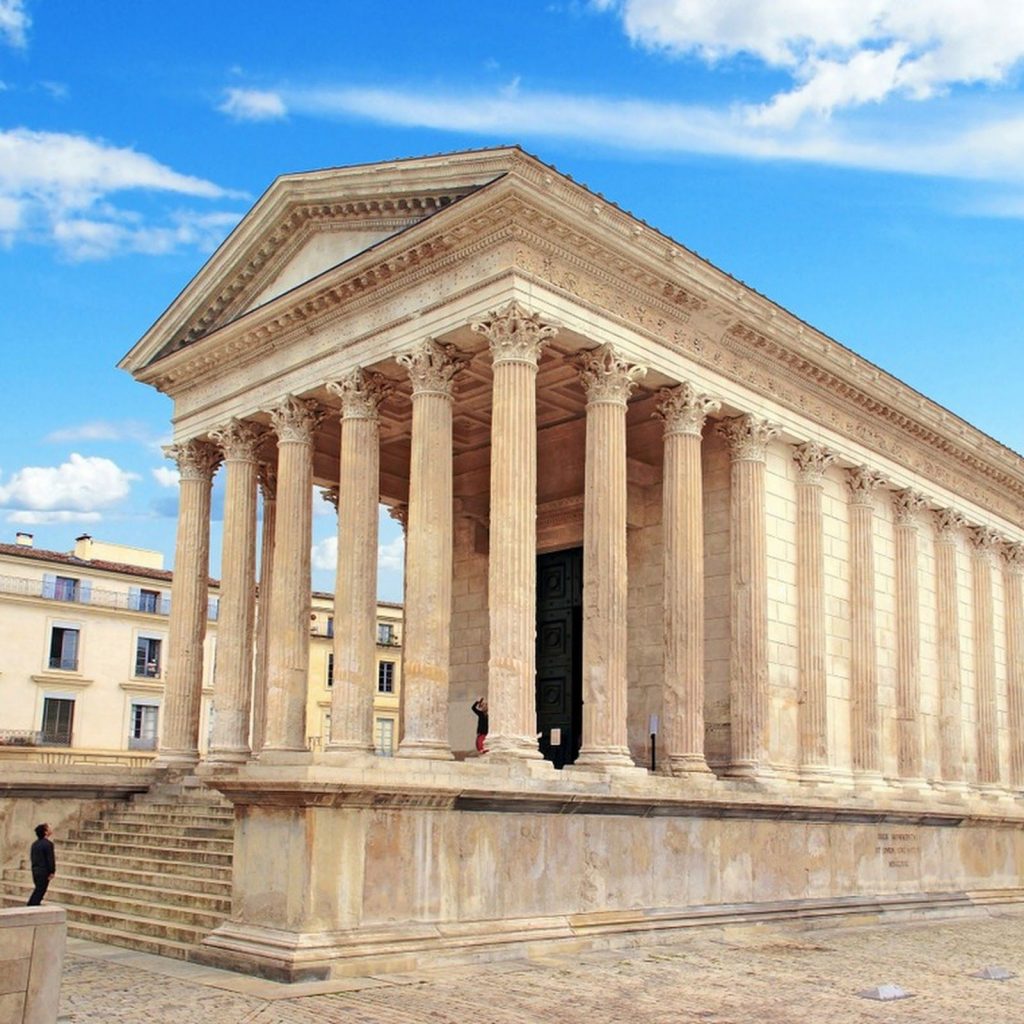

Normally they placed their temples on very high podium
whose staircase was located in the axis of the door of the
cella. They usually were pseudoperiptera, with the lateral
columns attached to the wall of the cella.
In its temples, the Roams used the Greek orders subjectin them to modifications. The orders more used were:
- Doric
- Ionic
- Corinthian
- Tuscan
- Composite
On the other hands,
They took elements from other Etruscan villages: arch and
vaultand they developed domes to cover buildings solving the
technical problems of the Greeks.
The Pantheon of Rome (118-128 CE) is the religious building that best represents the achievements of Rome.
CIVIL WORKS
Romans were specialists in the design of infrastructures such as:
- SEWAGE NETWORKS
- AQUEDUCTS
- ROADS
- BRIDGES
- WALLS
PUBLIC BUILDINGS
Romans were specialists in the design of infrastructures such as:
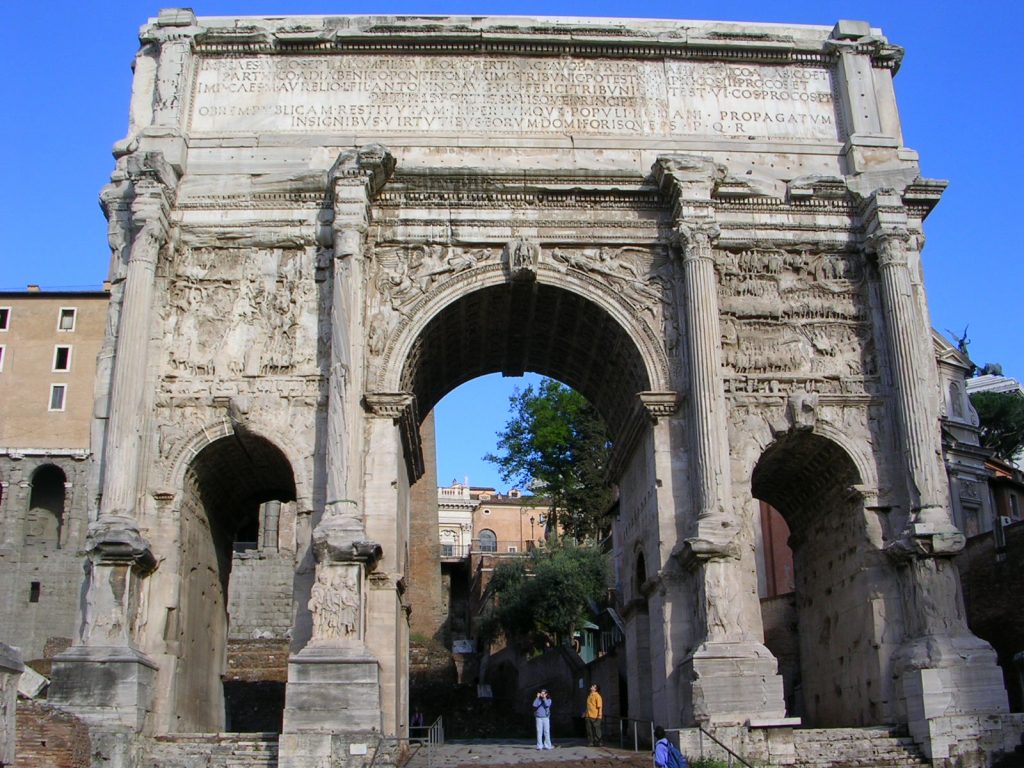
- TRIUMPHAL ARCHES
They are ceremonial works and a source of architectural and sculptural details. One example of it is the arch of Constantine.
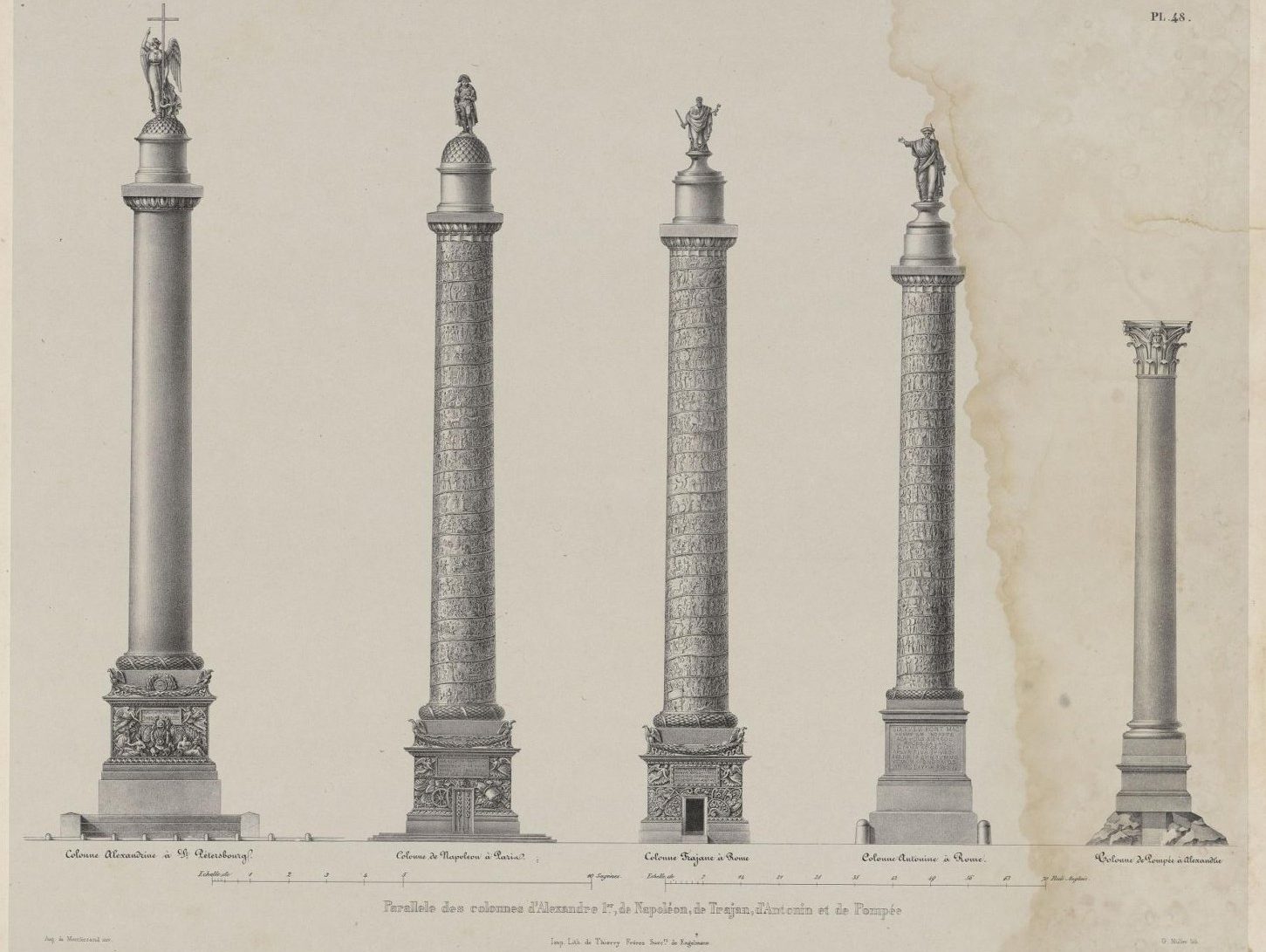
- COMMEMORATIVE COLUMNS
They are monuments erected to commemorate an important event, such as a military victory. One example of it is the Trajan’s column.
- THERMAL BATH
They played an important social role. The biggest served as baths, a place to exercise the body, a library, a school, a place for commercial relations, a place for the exhibition of sculptures, etc…
PARTS:
- Apodyterium
- Tepidarium
- Caldarium
- Frigidarium
- Natatio
- Palaestrae
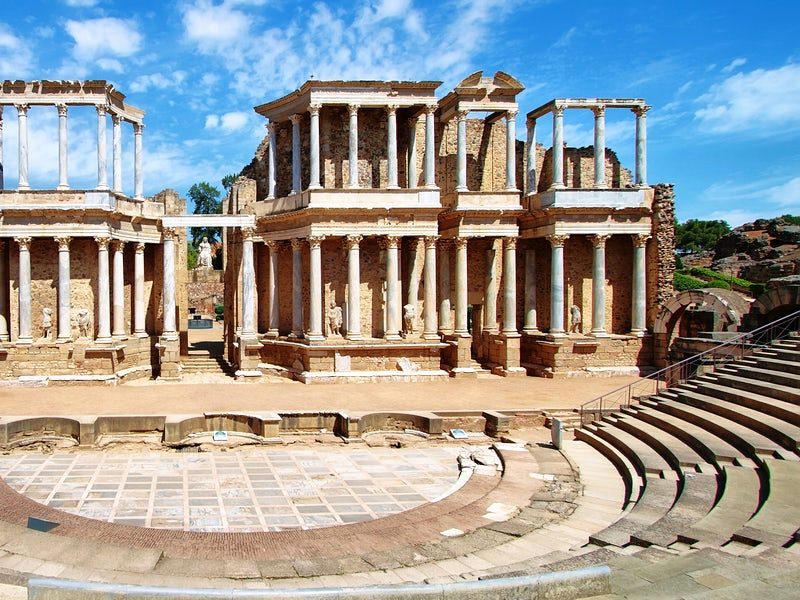
- THEATRE
They were perfectly semi-circular and their steps were built on a radial system of inclined concrete vaults raised on stone pillars. Their function was to perform theatrical Greek and Roman plays, withoutreligious or educational purposes. The main parts of a theatre were: Scænæ, Orchestra and Cavea.
- AMPHITHEATRE
The amphitheatres are the main Roman architecture’s innovation. They present a double theatre with elliptical scene and a continuous grandstand.
They were dedicated to fights between gladiators with beasts, or between them, and other similar mass spectacles.
The most known amphitheatre is the Colosseum in Rome.
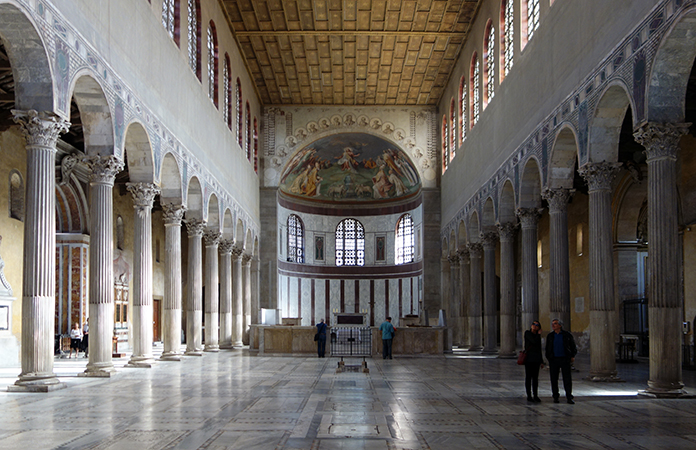
- BASILICA
The basilicæ were conceived as courts of justice for legal proceedings. They were usually rectangular, with central nave and aisles with a stage and apse at each of the two ends.
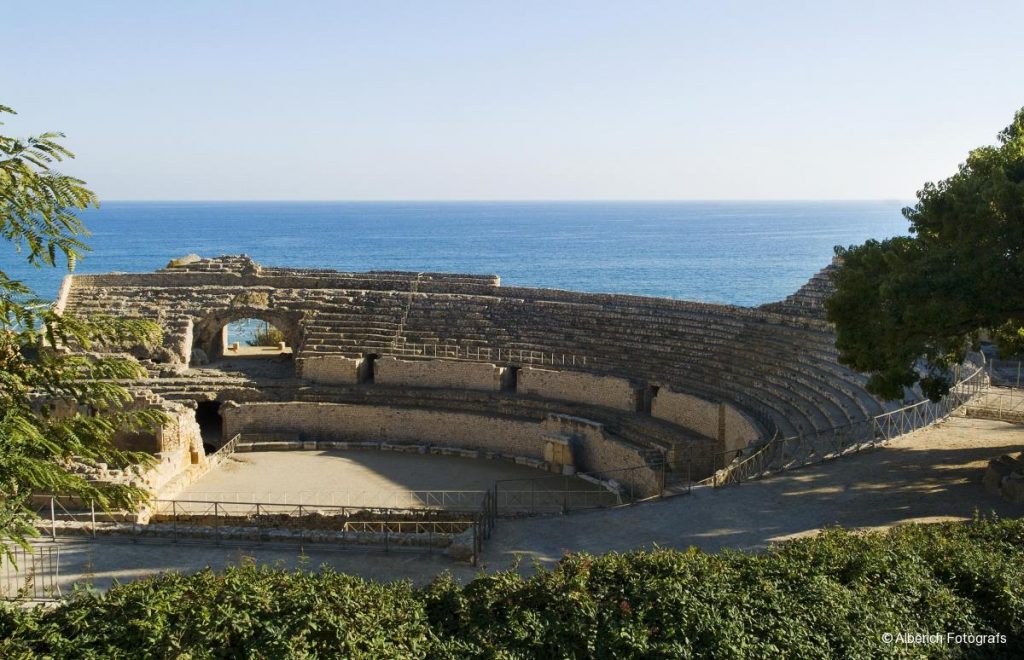
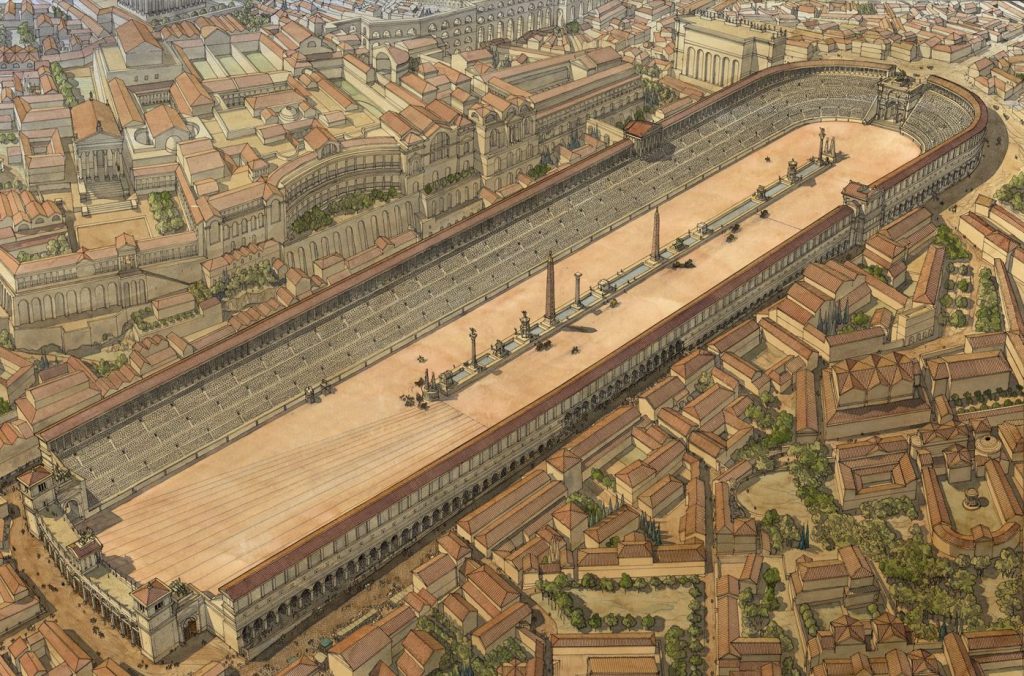
- CIRCUS
The Roman circus was destined for races, gladiatorial combats, shows and performances. An example of it would be The Circus Maximus of Rome, which had a capacity of 385.000 spectators.







PRIVATE BUILDINGS
- DOMUS

They were the habitual dwelling of the richest families. They were mainly decorated by mosaics, paintings and sculptures and they has a lot of facilities such as water, sewage and heating.
- INSULA
The insulæ were the dwellings of the plebeians who constituted the most numerous part of the population. They were buildings of three or four floors subdivided in different flats. The ground floor was used for tabernæ, shops
and businesses. They were built with low quality materials and wood.
Flats were divided into two premises, one for cooking and the
other for sleeping. They were often occupied by several
families at the same time. They had no heating, so there was
a fire in the middle of the kitchen for both cooking and
heating.

CITIES
Romans structured the city with an orthogonal planning. The first Roman cities and those that emerged from the Greek colonies had plots of streets in the form of more or less irregular rectangles, but later more regular city blocks were made.
-In the heart of the city was the forum.
-The basilica was one of the main buildings of the forum.
-The two main orthogonal streets were drawn from the forum: CARDUS and DECUMANUS.
-They had a system of walls and fortified gates.
This design continues in many cities nowadays.